Utilizando MkDocs en tu propio computador¶
Requirement:¶
MkDocs:¶
Get it in https://www.mkdocs.org/¶
- Follow the instructions below in section Building your project documentation
For Latex-kind and Maths¶
python-markdown-math
Get it (install using pip) as mentioned in: https://github.com/mitya57/python-markdown-math
Once you get those installed:
You can follow this instruction:
git clone https://gitmilab.redclara.net/tutoriales/tutorial-mkdocs.git
cd tutorial-mkdocs
mkdocs serve
To put it in App, you need to generate HTML by:
mkdocs build
Building your project documentation¶
MkDocs is a fast, simple and downright gorgeous static site generator that's geared towards building project documentation. Documentation source files are written in Markdown, and configured with a single YAML configuration file.
Mkdocs installation¶
- Prerequisite: Python and Pip
In order to manually install MkDocs you'll need Python installed on your system, as well as the Python package manager, pip. You can check if you have these already installed from the command line:
On Windows:
C:\Users\User>python --version
Python 3.5.4
C:\Users\User>pip --version
pip 9.0.1
On MacOS or Linux
$ python --version
Python 2.7.2
$ pip --version
pip 1.5.2
- Installing Python
Install Python by downloading an installer appropriate for your system from python.org and running it.
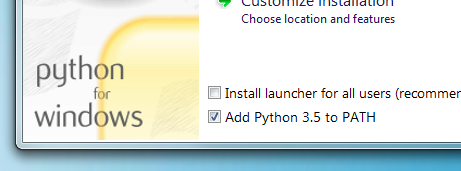
Note: If you are installing Python on Windows, be sure to check the box to have Python added to your PATH if the installer offers such an option (it's normally off by default).
- Installing Pip
If you're using a recent version of Python, the Python package manager, pip, is most likely installed by default. However, you may need to upgrade pip to the lasted version:
pip install --upgrade pip
If you need to install pip for the first time, download get-pip.py. Then run the following command to install it:
python get-pip.py
- Installing MkDocs
Install the mkdocs package using pip:
pip install mkdocs
You should now have the mkdocs command installed on your system. Run mkdocs--version to check whether successfully installed.
On Windows:
C:\Users\User>mkdocs --version
mkdocs, version 1.0.4
$ mkdocs --version
mkdocs, version 0.15.3
Getting started to edit¶
- Clone this documentation to your device by git
Clone with https:
git clone git clone https://github.com/LA-CoNGA-MiLab-RedClara/tutorial-mkdocs.git
cd tutorial-mkdocs
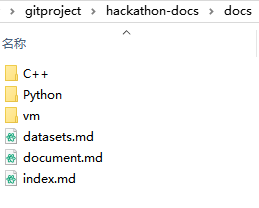
In your docs folder, you will see a configuration file named mkdocs.yml, and a folder named docs that will contain your documentation source files.

Right now the docs folder just contains all the documentation pages, such as index.md, datasets.md and the folders where the pages are saved.
MkDocs comes with a built-in dev-server that lets you preview your documentation as you work on it. Make sure you're in the same directory as the mkdocs.yml configuration file, and then start the server by running the mkdocs serve command:
C:\Users\User\tutorial-mkdocs>mkdocs serve
INFO - Building documentation...
INFO - Cleaning site directory
[I 190705 15:13:53 server:296] Serving on http://127.0.0.1:8000
[I 190705 15:13:53 handlers:62] Start watching changes
[I 190705 15:13:53 handlers:64] Start detecting changes
Open up http://127.0.0.1:8000/ in your browser, and you'll see the pages you cloned being displayed:

Use the editor you like to edit the files in docs and your changes will be displayed when saving them.
Using the Git to commit your changes¶
By far, the most widely used modern version control system in the world today is Git. In Git, every developer's working copy of the code is also a repository that can contain the full history of all changes.
Prerequisites:
- Download and install Git
- Apply for a Gitlab account
The working flow of Git:
- Initialise your repository with
git init[directory] - Clone a repository onto your local machine with
git clone [URL] - Edit the docs using Mkdocs
- Stage all changes for the next conmmit with
git add [directory] - Commit the staged snapshot with
git commit -m ["commit message"] - If others have modified it, you can check the updates with
git fetchand update the resource withgit pull. - Show unstaged changes between your index and working directory with
git diff - Review your changes before submitting with
git status - Push your changes to the remote Gitlab repository with
git push

Reference to git cheat sheet for details